React Hooks 源码概览
前言
这篇开始将会开始 Hooks 的源码实现,也是拖了很久没有动笔的部分了....
先说说看为什么会有 React Hooks?
在没有 hook 之前,函数式组件只能接受 props,渲染 UI 视图,以及触发父组件传来的事件。所有的处理逻辑都需要编写在类组件中,这就造成了类组件逻辑混乱、难以复用等问题
React Hooks 就是诞生于这样的背景下
所有 React Hooks 的出现原因可以归结为以下三点:
- 让函数式组件能够做类组件的工作,拥有状态,能够处理副作用、能够做数据缓存
- 解决逻辑复用难的问题。
- 放弃面向对象编程,拥抱函数式编程。
但是这也不是说,Function Component 就一定会比 Class Component 会更好,单纯的谈这件事也很不公平,这应该要落地到业务中去衡量是采用 FC 还是 CC,FC 对于业务组件的编写会更加的友好,CC 有更为丰富的生命周期函数,因此这件事没有对错之分,只有哪个更加的合适
这篇是 Hooks 源码的导读,我们先来看看 React 中大体是如何实现的呢?
这一篇会分为几个部分去讲
- 首先先讲讲在 hooks 设计中会使用到的数据结构
- 然后会简单讲讲 hooks 的入口,以及从使用到触发的流程
- 后面的文章都会介绍每个 hook 的原理,如何设计的,如何被调度、被处理的
Hooks 相关的数据结构
注意
这里临时再补多一部分的内容,在写后面的内容的时候,重新阅读了一下这几篇,发现还是有一些门槛的,因此先了解一下一些 Hooks 相关的数据结构是如何设计的
Hook
每一个 hooks 方法都会生成一个特定类型为 Hook 的对象,用来存储一些信息,许多的 Hooks 对象,会被连接形成 Hooks 链表,挂到 Fiber 的 memoizedState 字段上
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js
export type Hook = {|
memoizedState: any, // 上次渲染时所用的 state
baseState: any, // 已处理的 update 计算出的 state
baseQueue: Update<any, any> | null, // 未处理完的 update 队列
queue: UpdateQueue<any, any> | null, // 当前出发的 update 队列
next: Hook | null, // 指向下一个 hook,形成链表结构
|};例如我们调用两个 useState
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const [num, setNum] = useState(1)则 hook 链表的结构会是这样的
{
memoizedState: 0,
baseState: 0,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: {
memoizedState: 1,
baseState: 1,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
}
}同时不同的 hook 对应的 Hook 对象是不一样的,在 memoizedState 中存放的数据也是不一样的,这些我们可以在官网以及 React Devtools 工具上能感知到
- useState 存放的是 State
- useEffect 存放的是一个 effect 对象,在 devtools 上表现出来就是一个 fn
- useRef 存放的就是一个包含 current 的对象
- useMemo 存放的就是它的回调和依赖项数组
Update & UpdateQueue
Update 和 UpdateQueue 是存储 useState 的 state 及 useReducer 的 reducer 相关内容的数据结构。
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js
type Update<S, A> = {|
lane: Lane, // 优先级
// reducer 对应要执行的 action
action: A,
// 触发 dispatch 时的 reducer
eagerReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null,
// 触发 dispatch 是的 state
eagerState: S | null,
// 下一个要执行的 Update
next: Update<S, A>,
// react 的优先级权重
priority?: ReactPriorityLevel,
|};
type UpdateQueue<S, A> = {|
// 当前要触发的 update
pending: Update<S, A> | null,
// 存放 dispatchAction.bind() 的值
dispatch: (A => mixed) | null,
// 上一次 render 的 reducer
lastRenderedReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null,
// 上一次 render 的 state
lastRenderedState: S | null,
|};每次调用 useState 或者 useReducer 的 dispatch 时,都会生成一个 Update 类型的对象,并将其添加到 UpdateQueue 队列中。
最后 react 会遍历 UpdateQueue 中的每个 Update 去进行更新。
Effect
Effect 结构是和 useEffect 等 effect hooks 相关的,先看一下它的结构:
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js
export type Effect = {|
tag: HookFlags, // 标记是否有 effect 需要执行
create: () => (() => void) | void, // 回调函数
destroy: (() => void) | void, // 销毁时触发的回调
deps: Array<mixed> | null, // 依赖的数组
next: Effect, // 下一个要执行的 Effect
|};当我们的函数组件中使用了如下的 useEffect 时:
useEffect(() => {
console.log('create');
return () => {
console.log('destroy');
};
}, []);对应的 Hook 如下:
{
memoizedState: {
create: () => { console.log('create') },
destroy: () => { console.log('destroy') },
deps: [],
// ...
},
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
}这就是和 Hook 这部分强相关的三个对象
Hooks 源码入口
在 packages/react/src/React.js 文件中,引入了 ReactHooks 导出的 Hooks
import {
...
useTransition,
useDeferredValue,
useId,
useCacheRefresh,
} from './ReactHooks';看到 ReactHooks,里面定义了这些 hook 的实现入口
// 截选
export function useState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
export function useReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useReducer(reducer, initialArg, init);
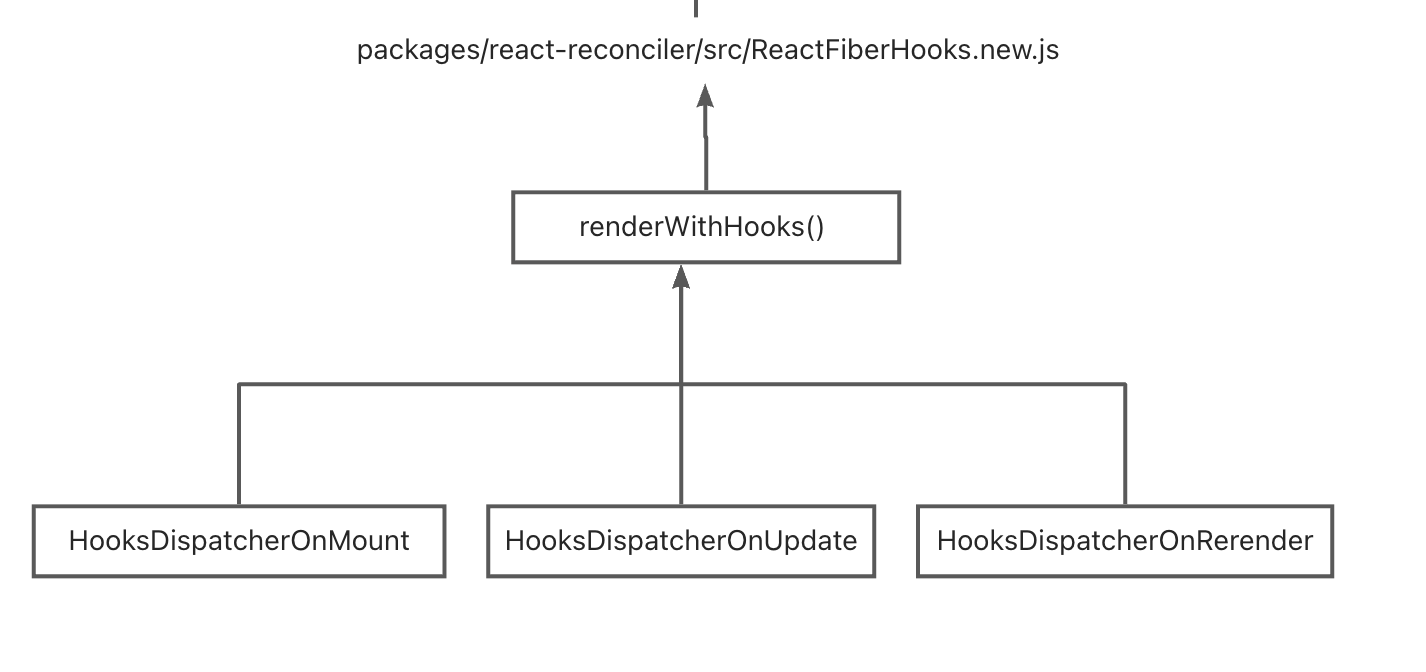
}观察每个 hook 函数,会发现每个 hook 函数都调用了 resolveDispatcher() 函数,这个函数返回的是 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current ,全局搜索可以发现在 renderWithHooks 中会对它进行赋值
所有函数组件的触发是在 renderWithHooks 方法中
在 fiber 调和过程中,遇到 FunctionComponent 类型的 fiber(函数组件),就会用 updateFunctionComponent 更新 fiber
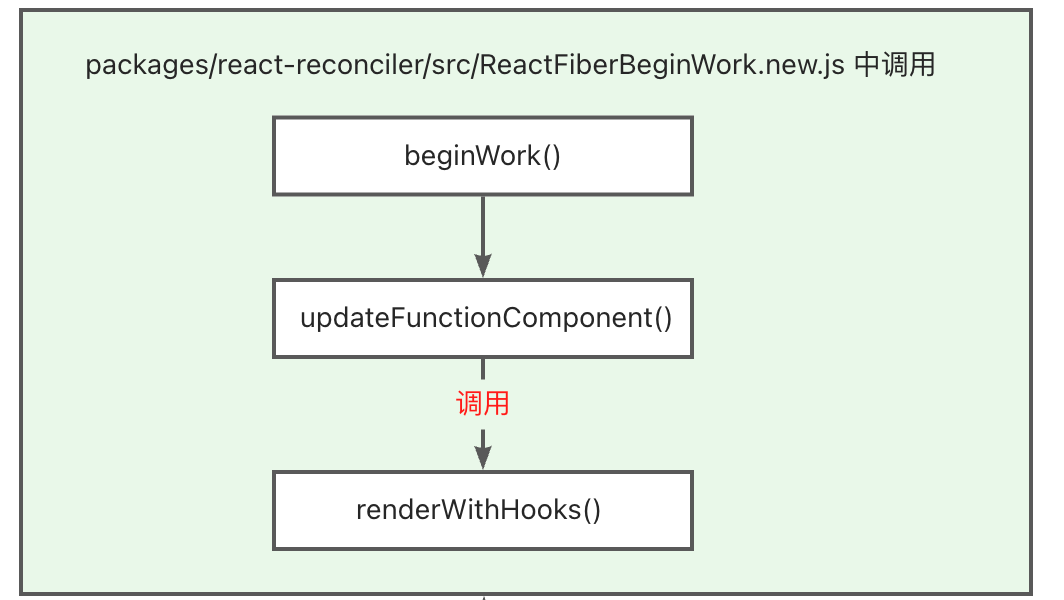
在 updateFunctionComponent 中,调用 renderWithHooks 获取函数组件的 children,然后赋值给 nextChildren,最后在 reconcileChildren() 中将 nextChildren 挂载到了 workInProgress的child 属性上。
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
props: Props,
secondArg: SecondArg,
nextRenderLanes: Lanes,
): any {
...
if (__DEV__) {
// ...
} else {
// 根据状态挂载不同的 dispatcher ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 上
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
// 组件挂载时 hook 的初始化
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
// 组件更新时 hook 的初始化
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
}
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// 检查在渲染阶段是否更新
if (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass) {
let numberOfReRenders: number = 0;
do {
...
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = __DEV__
// 开发环境
? HooksDispatcherOnRerenderInDEV
: HooksDispatcherOnRerender;
children = Component(props, secondArg);
} while (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass);
}
// 错误捕获处理
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
...
return children;
}根据上面的代码我们可以总结出 3 点,也就是 Hooks 对象在 React 中存在的 4 种形态,
- 在组件挂载时,将
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current赋值为HooksDispatcherOnMount,这时候 hooks 的作用就是建立 Fiber 和 hooks 的桥梁,初次建立 Fiber 和 Hooks 的关系。 - 在组件更新时,将
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current赋值为HooksDispatcherOnUpdate,这个形态hooks 需要去获取更新维护状态。 - 在
render阶段,将ReactCurrentDispatcher.current赋值为HooksDispatcherOnRerender - 在函数组件外部调用 hooks 时,也就是报错形态,将
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current赋值为ContextOnlyDispatcher,react 会抛出异常
总结一下这个 renderWithHooks 函数的主要工作如下
- 首先会存一些数据,
memoizedState用来存放hooks的信息,updateQueue存放副作用链表,在 commit 阶段去执行副作用 - 判断组件是 update 还是 mount 流程,给
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current赋不一样的值 - 在执行 FC 之前,会将
current赋值为HooksDispatcherOnRerender, - 调用
Component(props, secondArg)真正的执行函数组件,依次执行每个 hooks - 在函数组件执行完,将 current 赋值为
ContextOnlyDispatcher
React 就是通过赋予 current 不同的 hooks 对象达到监控 hooks 是否在函数组件内部调用。
不同的 Hooks 对象
在前面不同的阶段会赋值不同的 Hooks 对象,这里面每个 hooks 对应的方法都不一样
const HooksDispatcherOnMount = { /* 函数组件初始化用的 hooks */
useState: mountState,
useEffect: mountEffect,
...
}
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate ={/* 函数组件更新用的 hooks */
useState:updateState,
useEffect: updateEffect,
...
}
const HooksDispatcherOnRerender: Dispatcher = { /*组件render阶段赋值ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 的对象*/
useCallback: updateCallback,
useContext: readContext,
...
};
const ContextOnlyDispatcher = { /* 当hooks不是函数内部调用的时候,调用这个hooks对象下的hooks,所以报错。 */
useEffect: throwInvalidHookError,
useState: throwInvalidHookError,
...
}例如 mount 时的 useState 会调用 mountState ,update 时会调用 updateState,就是通过调用不同的 Hooks 对象来控制的
因此,ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 上挂载的是组件在相应阶段的 Hook 处理函数,这些处理函数是在 renderWithHooks函数中挂载到 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current上。
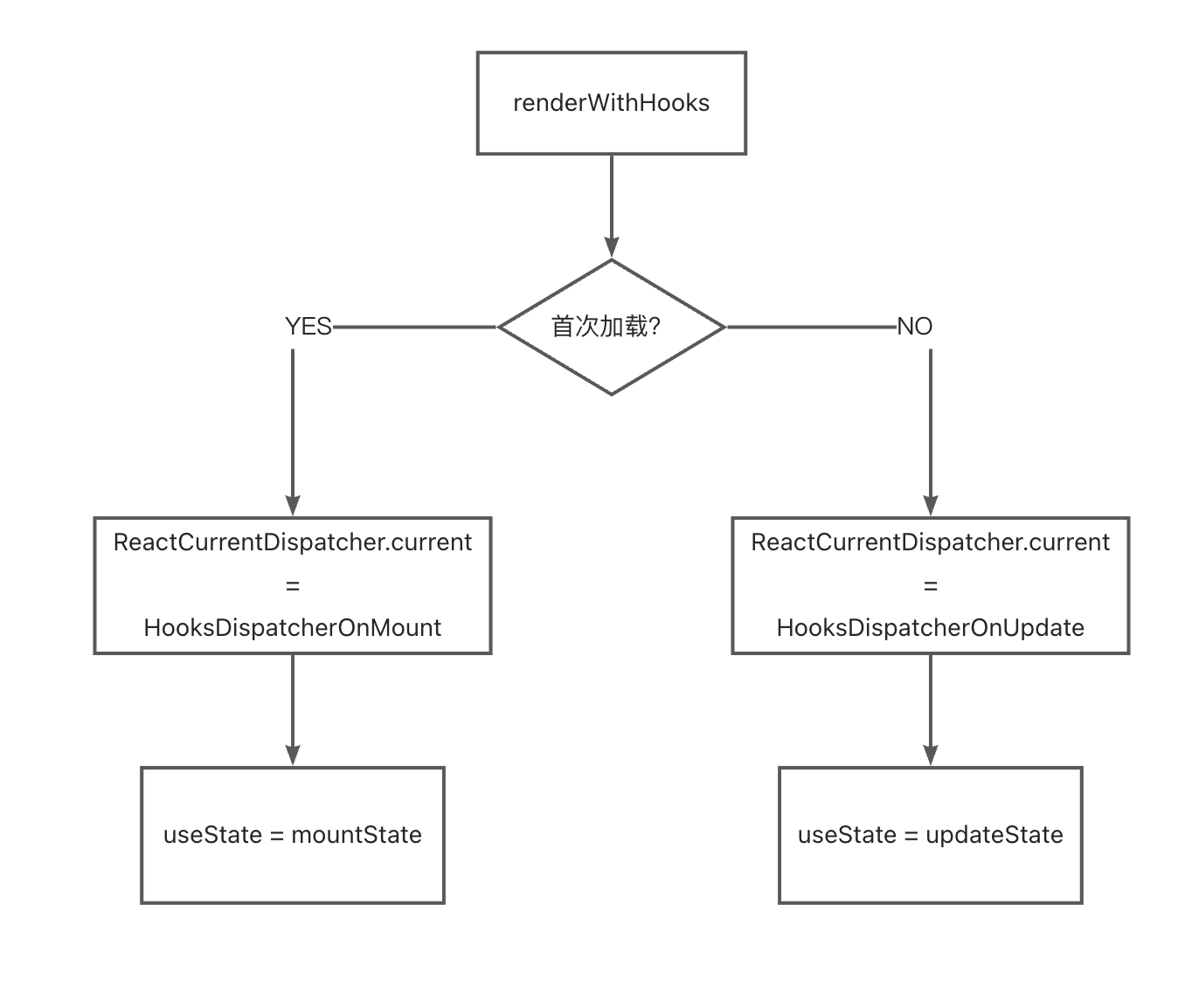
示例
我们以 useState 为例讲解 hook 的挂载。
如果 current 为空,说明是首次加载,将 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState 赋值成 HooksDispatcherOnMount.useState
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.new.js
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
// ...
useState: mountState,
// ...
};如果 current 不为空,说明是在组件更新阶段,ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState 赋值成 HooksDispatcherOnUpdate.useState
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.new.js
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
// ...
useState: updateState,
// ...
};因此,我们流程就可以分为
总结
本文,介绍了 Hooks 的入口以及入口函数 renderWithHooks。
当我们调用某个 hook 时,实际上调用的是挂载在 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 属性上的对应的 hook 处理函数,每种形态都对应着不同的 dispatch 方法!